Ester Chemistry - Unveiling Aromatic Secrets
You know, sometimes the most interesting things are hiding right under our noses, like certain chemical compounds that bring so much joy to our daily lives. We are talking about something called an ester, which, in a way, is a pretty fascinating little molecule. It’s a compound that comes from an acid, whether that acid is organic or something inorganic, where a hydrogen atom from a specific part of the acid gets swapped out. It’s a bit like a tiny chemical dance, if you think about it, where one part steps aside for another to take its place.
These compounds, esters, are actually a class of organic compounds that have a rather neat trick up their sleeve. When they meet water, they tend to react in a particular way, giving us alcohols and either organic or inorganic acids. It’s a process that, in some respects, shows how versatile these molecules really are. The ones we come across most often, or perhaps hear about the most, are those that come from what we call carboxylic acids. They are, you know, the main characters in the ester story for many everyday applications.
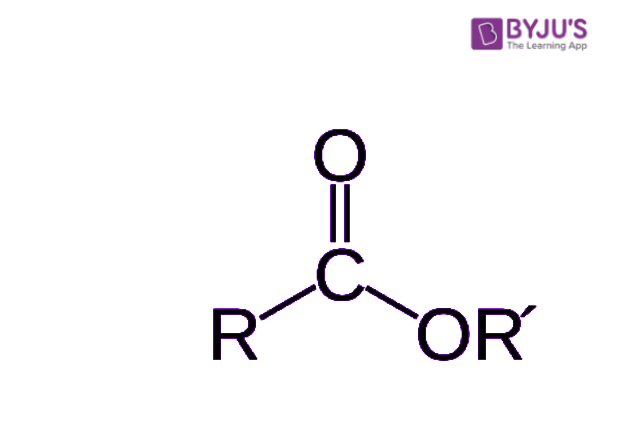
So, what makes an ester, well, an ester? Basically, it’s an organic compound where the hydrogen in a specific part of the compound, the carboxyl group, is replaced with a hydrocarbon group. This tiny change, you see, is what gives esters their unique characteristics and makes them so useful. They are derived from carboxylic acids, as we mentioned, and this basic structure is what gives them their identity. It’s a fundamental building block, really, that helps us understand where they fit in the grand scheme of chemistry.
- Amiyah White
- Hillside Athens
- Culture Shock Chicago
- Blue Lagoon Playa Del Carmen
- Hayden Panettiere Big Tits
What Exactly is an Ester, Anyway?
When we talk about an ester, we're really talking about a chemical compound that comes from an acid. It's like taking a recipe for an acid and making a slight, but important, change. You see, the hydrogen atom, the little 'H' in the chemical formula, from at least one of the acidic hydroxyl groups, which is that ‘-OH’ part of the acid, gets replaced. It’s almost as if that hydrogen atom steps aside, allowing something else to take its spot. This swap is what makes an ester distinct from its parent acid, and it’s a very common process in the chemical world, actually.
Esters are, in their essence, a particular group of organic compounds. They have this interesting characteristic where, when they interact with water, they tend to break down. This breaking down, or reaction, gives us two new things: alcohols and either organic or inorganic acids. It’s a pretty neat way for molecules to transform, and it's a process that happens quite a bit in nature and in industrial settings. The most well-known esters, the ones you might hear about more often, are those that come from carboxylic acids. These are, in a way, the stars of the ester family, given their widespread use and presence.
So, what does an ester look like on a molecular level? Well, you can identify its general structure. It’s an organic compound where the hydrogen that would normally be in the compound's carboxyl group gets swapped out for a hydrocarbon group. This hydrocarbon group is just a chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms, which, you know, can be short or long. This specific arrangement is what defines an ester. They are, as we've said, derived from carboxylic acids, and this connection is key to understanding their properties and how they behave. It’s a fundamental piece of chemical architecture, really.
How Do We Talk About These Ester Compounds?
Naming these compounds, the esters, can seem a bit involved at first, but it follows some pretty clear rules. There are, for instance, common names that people use, especially for those esters we encounter regularly. It’s a bit like having nicknames for friends, you know? These common names are often simpler and easier to remember, especially if you’re not a chemist. They just make sense in everyday conversation, really. For example, some fruit flavors are due to specific esters, and their common names often relate to the fruit itself, which is kind of helpful.
Then there’s the more formal way of naming esters, which is according to the IUPAC system. This system is, you know, the international standard for naming chemical compounds, and it ensures that chemists all over the world can understand exactly which molecule is being discussed. It’s a bit more structured, certainly, and involves looking at the lengths of the carbon chains in the molecules. The names for esters include prefixes that tell us how long these carbon chains are, which is pretty important for identification. It’s a very precise way of communicating, honestly.
For example, let’s consider methyl butanoate. This particular ester is, as a matter of fact, found in pineapple oil, and it’s what gives pineapple some of its distinctive smell and taste. Its name, methyl butanoate, tells us a lot about its structure. Or, take isopentyl acetate, which is what gives bananas their characteristic aroma. These names, while they might sound a bit technical, are really just descriptions of the molecules themselves. They help us, you know, connect the chemical structure to the real-world properties, like smells and flavors. It’s quite fascinating, actually, how specific these connections are.
What Makes an Ester Smell So Good?
It’s almost like magic how certain chemicals can create such delightful smells, and esters are truly masters of this. They are used, very, very often, in the flavor and fragrance industry, which is probably where most people encounter them without even realizing it. Think about the sweet smell of fruits or the lovely scent of flowers – a lot of that comes down to the presence of specific esters. They are, in a way, nature’s own perfumers, crafting these aromatic experiences for us to enjoy. It’s pretty remarkable, if you ask me, how such small molecules can have such a big impact on our senses.
Esters, you know, are usually derived from carboxylic acids, and this particular origin gives them many of their scent-producing qualities. The way their atoms are arranged, especially with that second oxygen atom bonding to another carbon atom, as you might see in a diagram, is key. This structure allows them to interact with our scent receptors in very specific ways, triggering those familiar and pleasant aromas. It’s a bit like a key fitting into a lock, where the ester molecule fits perfectly into a receptor in our nose, creating that sensation of smell. It’s a truly intricate system, in fact.
Consider, for instance, how methyl butanoate is found in pineapple oil. That’s why pineapples smell like pineapples! Or take isopentyl acetate, which is the reason why bananas have their distinct, sweet smell. These are just a couple of examples, but there are so many more. Esters are responsible for the smells of apples, pears, strawberries, and even some artificial flavors in candies and drinks. They are, basically, the secret ingredients behind many of the wonderful smells and tastes that we experience every day. It’s a testament, really, to the incredible diversity of chemical compounds and their roles.
Are There Any Special Ester Names We Should Know About?
When we talk about esters, sometimes there are older names that pop up, names that have been around for a long time. One such example is glyceryl. You might not hear it as much in everyday conversation, but in certain contexts, especially older texts or specialized fields, it’s still used. But the truth is that almost everybody calls it, not surprisingly, by its old name of glyceryl. It’s a bit like how some old towns still have their original names even after they’ve been officially renamed; people just stick with what they know. It’s a kind of historical echo in the world of chemistry, really.
This particular compound, glyceryl, is, you know, pretty important because it’s the backbone of fats and oils, which are essentially a type of ester. These are called triglycerides, and they are absolutely vital for life. So, while the name glyceryl might seem a bit old-fashioned, it points to a very significant group of esters that play a huge role in biology and nutrition. It’s a good example of how chemical naming can sometimes have a bit of a history to it, and how older terms can persist even when newer, more systematic ones are introduced. It’s all part of the language of science, in a way.
Understanding these different names, both the common ones and the more formal ones, helps us to really grasp the subject. It’s like learning different dialects of a language; they all convey the same meaning, but in slightly different ways. Whether we’re talking about methyl butanoate making pineapple smell wonderful, or the older name glyceryl pointing to the building blocks of fats, it’s all about appreciating the diversity and utility of esters. They are, truly, a very interesting class of compounds with a lot to tell us about the world around us.
How Do Esters Fit Into Our Daily Lives?
Esters are, you know, far more present in our daily routines than many of us might realize. They are the silent contributors to many of the pleasant sensations we experience. For instance, when you peel an apple and that fresh, crisp scent fills the air, you’re experiencing the work of esters. Or, when you enjoy a piece of candy with a distinct fruity flavor, it’s highly probable that an ester is playing a key role in creating that taste. They are, basically, the hidden artists behind many of our favorite sensory experiences, which is pretty cool if you think about it.
Beyond just flavors and fragrances, esters also have other important jobs. They can be found in solvents, which are liquids that dissolve other substances. This makes them useful in things like paints, varnishes, and even some cleaning products. So, they’re not just about making things smell nice; they also perform very practical functions in various industries. It’s a testament, really, to their versatility and how their unique chemical structure allows them to be adapted for so many different purposes. They are, in a way, chemical workhorses, quietly getting the job done.
Think about the simple act of lighting a candle with a lovely scent. That scent is, more often than not, due to esters. Or consider the taste of a refreshing fruit juice; again, esters are probably involved. They are also present in natural fats and oils, which are absolutely essential for our bodies to function properly. So, from the food we eat to the products we use for cleaning or personal care, esters are, quite literally, everywhere. They are a fundamental part of the chemical tapestry that makes up our world, and their contributions are, honestly, pretty significant.
In short, we've taken a look at esters, those interesting chemical compounds that come from acids and play a big part in the world of smells and flavors. We talked about what they are, how they're structured, and how we name them, whether it's by common names or the more formal IUPAC system. We also touched on how important they are in the flavor and fragrance industry, giving us those wonderful fruity scents and tastes we love. Finally, we considered how some older names, like glyceryl, still pop up, reminding us of the rich history behind these everyday molecules.
- Giusy Buscemi Nuda
- Christina Garcia Covey
- Amiyah White
- Davide Buonarroti
- Adirondack Elopement Photographer

File:Ester.svg - Wikimedia Commons
/ester-59134cd83df78c9283519859.png)
What Is an Ester in Chemistry?
Ester - Definition, Structure, Esterification along with Properties & Uses